Kodali, Prakash Babu. "People’s perceptions on COVID-19 vaccination: an analysis of twitter discourse from four countries - Scientific Reports." Nature. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-41478-7Summary
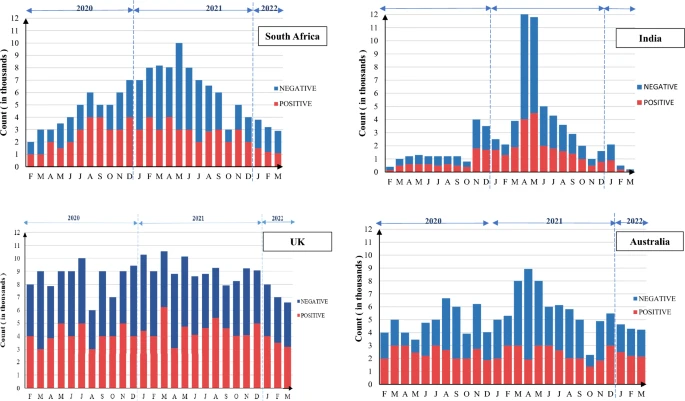
The study aimed to understand the attitudes and perceptions of Twitter users from four countries (India, South Africa, the UK, and Australia) towards COVID-19 vaccinations. A sentiment analysis of 663,377 tweets from October 2020 to September 2022 used the roBERTA python library. The analysis sorted tweets by sentiment, as “negative,” “positive,” or “neutral.” Additionally, 2,000 tweets (500 from each country) were analyzed thematically to explore how people see COVID-19 vaccines.
Key Findings and Evidence
Negative attitudes towards COVID-19 vaccines were highest in India (58.48%), followed by the UK (33.22%), Australia (31.42%), and South Africa (28.88%).
Positive attitudes were most common in the UK (21.09%).
Negative and positive sentiment tweets are not necessarily tied to whether someone supports vaccines. A negative tweet could come from someone who is lamenting a vaccine shortage.
Researchers identified eight overarching topics:
Vaccine shortages
Vaccine side-effects
Distrust in COVID-19 vaccines
Calls for vaccine equity
Awareness about vaccines
Debunking myths about vaccines
Evidence that vaccines work
Assurance that vaccines are safe.
Diving into anti-vaccine content
Vaccine Side Effects
Vaccine side effects are physical reactions that occur after receiving a vaccine. They are typically mild and temporary. Common side effects for many vaccines, including COVID-19, include pain at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea. These reactions are usually a sign that the body is building protection against the virus.
Reasons for Mistrust
Distrust in vaccines can stem from various sources:
Historical Context: Past unethical medical practices can lead to mistrust in medical interventions, including vaccines.
Misinformation: The spread of false information about vaccines, often amplified by social media, can sow doubts.
Rapid Development: The unprecedented speed of COVID-19 vaccine development, while a scientific triumph, led some to believe corners were cut (they weren’t).
Political and Economic Motivations: Perceived profit motives by pharmaceutical companies or political agendas can lead to skepticism.
Addressing this distrust requires transparent communication about the vaccine development process, its safety protocols, and the rigorous trials and reviews the vaccines underwent before approval.
Debunking Myths
Several myths surrounding the COVID-19 vaccines have been circulating, and debunking them is crucial for public health:
Alteration of DNA: mRNA vaccines (like Pfizer and Moderna) do not alter the DNA of those who receive them. They work by teaching cells to make a protein that triggers an immune response.
Microchips: There’s a conspiracy theory that vaccines contain microchips to track individuals. This is entirely false.
Infertility: No scientific evidence suggests that COVID-19 vaccines affect fertility in men or women. The most troubling claims are those that strike at deeply held fears that would take a long time to disprove from the individual’s perspective.
Natural Immunity Superiority: While getting infected with COVID-19 offers some immunity, the risk of severe disease and complications makes vaccination safer.
Vaccines and Illness: Some believe the vaccine can give you COVID-19. This is not true; the vaccines teach the immune system how to recognize and fight the virus.
Debunking these myths requires continuous efforts from health professionals, community leaders, and policymakers, using clear, evidence-based information and addressing concerns empathetically.
The steady flow of content making baseless claims can influence people and even when people know a claim is false, repeated exposure can affect them.
Implications
Understanding public sentiment toward COVID-19 vaccinations will be critical in addressing concerns. The varied attitudes across countries highlight the need for tailored communication strategies.
The themes identified can guide policymakers and health professionals in addressing concerns and promoting positive attitudes toward vaccination. The study also underscores the importance of social media platforms like Twitter in gauging public sentiment and shaping health communication strategies.
Source
Citation
@article{infoepi_lab2023,
author = {InfoEpi Lab},
publisher = {Information Epidemiology Lab},
title = {Twitter {Sentiment} {Analysis} on {COVID-19} {Vaccination}},
journal = {InfoEpi Lab},
date = {2023-09-01},
url = {https://infoepi.org/posts/2023/09/01-vaccine-twitter-four-countries.html},
langid = {en}
}